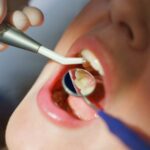
Today, older people are able to keep their teeth for many more years than in the past, and the average number of teeth retained increases with age, but this often does not prevent further dental problems from occurring. For these reasons, it is important to visit the dentist regularly.In this article, we list the most …
Today, older people are able to keep their teeth for many more years than in the past, and the average number of teeth retained increases with age, but this often does not prevent further dental problems from occurring. For these reasons, it is important to visit the dentist regularly.
In this article, we list the most common oral and dental problems and their solutions.
1. Tooth Decay
Decay can occur in adults and older people. This can occur in front of and around old fillings, crowns and bridges, on the surface of teeth that have not had problems before, or at the root of your teeth. As you get older, the roots of your teeth become softer and the risk of such problems increases.
How to Treat Tooth Decay?
You can try fluoride gels and mouthwashes, but if you want something more natural, you should eat a mineral-rich diet and get plenty of vitamin D. Or ask your dentist for prescription gels or polishes that you can apply to your teeth and tooth roots.
2. Dry mouth
Saliva protects our teeth against decay. But as you get older, if you are taking medication or have certain health problems, you may not produce enough saliva and your teeth may be at risk of tooth decay and gum disease. The minerals found in saliva, calcium and phosphate, prevent demineralization and fight tooth decay. So how do you know if you have a dry mouth? A sticky feeling in your mouth, trouble swallowing, a dry throat and dry, chapped lips can be signs of a dry mouth. If you have a metallic taste in your mouth or persistent bad breath, you may have dry mouth. Dry mouth is often caused by medication and the older people get, the more medication they need to take. Dry mouth can also be caused by smoking or health problems that damage the salivary glands.
Treatment for dry mouth?
If you have dry mouth, you should try to increase saliva production. You can drink plenty of water throughout the day or chew sugar-free xylitol gum. Often this is not enough to get enough saliva flowing and your mouth can be at risk. Your dentist can also help you to increase saliva by prescribing or formulating a prescription saliva-generating product.
3. Gum Diseases
If your gums are swollen, red or bleed easily, you may have gingivitis (gingivitis), an early form of gum disease that can be progressive and dangerous. Untreated gum disease develops into periodontitis when the gums recede from the teeth and form pockets that can become infected. When gum disease is left unchecked and untreated, it can lead to bone loss in your jaw and eventually the loss of your teeth.
Your risk of developing gum disease increases especially if you do not pay enough attention to oral hygiene, have crowns, have had unsuccessful dental procedures, smoke and use medication, dry mouth and being in the postmenopausal period.
Treatment of Gum Diseases
The best remedy for this condition is regular visits to the dentist and hygienist. By regular, I mean more often than the generally recommended twice a year, as inflamed, infected gums may need to be treated more often for this condition.
4. Oral Cancer
The incidence of oral cancer increases with age and this serious disease is often associated with smoking and alcohol use. Recently, cases of oral cancer have become common and it has been discovered that the Human Papillomavirus can also cause this condition.
Oral Cancer Treatment
Only half of people with oral cancer survive. Early diagnosis increases the chances of survival and increases the chance of survival to eighty percent. Your dental examination should include oral cancer tests. Your dentist should hold your tongue and check for soft tissue in your mouth, throat and jaw.
5. Malocclusion – Incorrect Closure
As you age, your teeth shift and this can cause problems beyond appearance. These teeth are harder to clean and more vulnerable to decay and gum disease. Uneven teeth can also damage supporting tissue and bone. Overlapping and moving teeth lead to incorrect bites, make chewing difficult, and cause nighttime clenching and locking. Older people are also more prone to gum disease, increasing the likelihood of tooth loss.
Malocclusion Jaw Malocclusion Treatment
If your teeth have shifted, you may need to wear braces, spacers or wires, for which you should visit your dentist. Your dentist may not consider these to be necessary, but you should still ask your dentist if you have this problem during your general check-ups. If you have this problem, you will need to visit your dentist more often for both cleaning and corrective treatments.
6. Teeth Clenching and Grinding
Teeth clenching and grinding is not a problem that starts late in life, but its effects become more pronounced with age. If you clench or grind your teeth while you sleep, you can damage the enamel and reach the dentin layer, which can lead to pain and decay. You can also crack or separate teeth with loose fillings, or damage crowns and bridges if you have them in your mouth. Teeth clenching and grinding worsen with age because your teeth overlap and your bite becomes uneven. Snoring and the development of sleep apnea in the elderly are also associated with teeth clenching.
Treatment of Teeth Clenching and Grinding
Our dentist can make a night guard or sleep apnea-snoring orthotic for you, so you can protect your teeth, fillings, crowns and bridges from damage while you sleep.